Addressing API Challenges with Gateway and Management System
APIs play a critical role in modern software development, enabling seamless integration across applications. As the demand for robust and efficient APIs grows, API teams need to address many concerns to ensure the successful development, deployment, and management of their APIs. In this article, we will explore the key challenges an API team needs to address and how API gateway and management system can help.
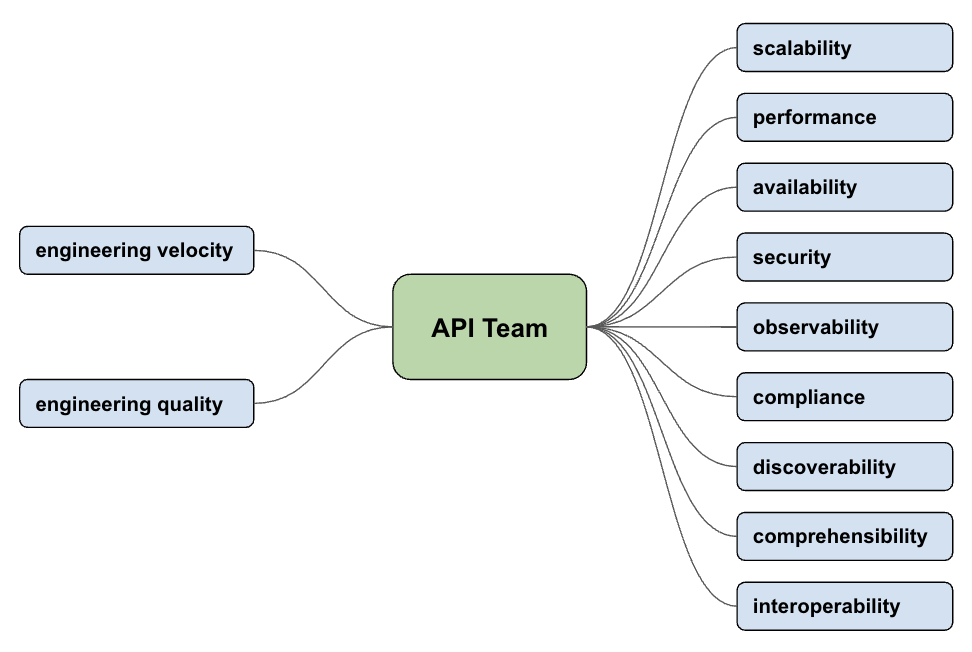
The Challenges
Let’s begin with the key challenges an API team faces on daily basis, without getting into the specifics for now.
API Gateway
An API Gateway is a server that acts as an intermediary between API clients (such as web or mobile applications) and backend service instances. Its primary function is to route API requests to the appropriate backend services, but it can also provide additional features to enhance and manage APIs.
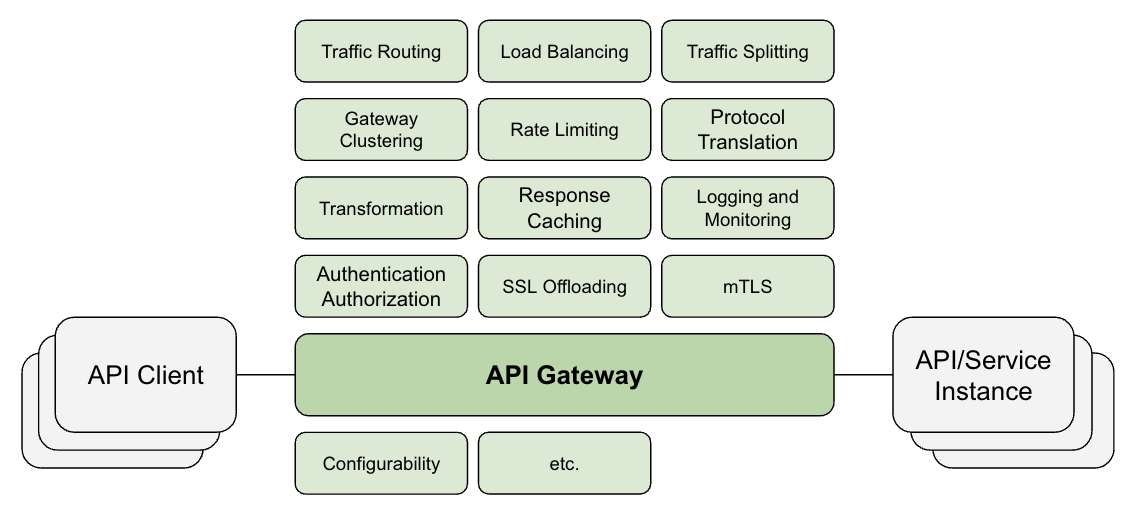
Some of these features include:
- Traffic Routing: Routing incoming requests to the appropriate backend services based on various factors such as URL patterns, client metadata, request content.
- Load Balancing: Distributing traffic among multiple backend services to ensure high availability and optimal performance.
- Traffic Splitting: Splitting and routing incoming requests to different clusters of backend services based on predefined ratio.
- Gateway Clustering: Having multiple API gateway instances to form a cluster serving client traffic.
- Rate Limiting: Controlling the number of requests a client can make to an API within a specific timeframe to prevent overloading the backend services.
- Protocol Translation: Translating between different API protocols (e.g., REST, SOAP, or GraphQL) or messaging protocols (e.g., HTTP, HTTPS, or WebSocket), allowing clients to use their preferred communication methods while interacting with backend services.
- Transformation: Transforming data formats between clients and backend services. For example, an API gateway can convert XML data from a legacy SOAP-based backend service to JSON for a modern client application and vice versa.
- Response Caching: Storing frequently requested data to reduce the load on backend systems and improve response times.
- Logging and Monitoring: Tracking API usage, performance, and errors to facilitate troubleshooting and analytics.
- Authentication and Authorization: Verifying the identity of API clients and controlling their access to specific endpoints based on predefined policies.
- SSL Offloading: Decrypting incoming SSL/TLS encrypted traffic before forwarding it to backend services and encrypting response from backend services before sending to client.
- mTLS (mutual TLS): Requiring both the client and the server to authenticate each other’s identities and ensuring that only trusted clients can access the API.
- Configurability: Offering the ability, typically in the form of administration API, to manage and configure API gateway, including routing rules, load balancing algorithms and policies, security policies, etc., etc.
API Management System
An API management system is a suite of tools and services designed to help organizations create, publish, maintain, monitor, and secure their APIs. It typically includes features like API design, documentation, versioning, analytics, and developer portal, as well as API access control and rate limiting. The goal of an API management system is to simplify the process of building and maintaining APIs while providing visibility into their usage and performance.
Key components of an API management system include:
- API design and documentation: Tools to define, design, and document APIs, often using specifications like OpenAPI.
- API lifecycle management: Support for creating, publishing, and versioning APIs, as well as deprecating and retiring them.
- API analytics and monitoring: Insights into API usage, performance, and errors, enabling organizations to identify and address potential issues.
- Developer portal: A centralized platform for API consumers (developers) to discover, learn about, and access APIs, typically including API documentation, authentication information, and usage examples.
- API access control and security: Features to define and enforce policies for API access, authentication, and authorization, as well as rate limiting and quota management.
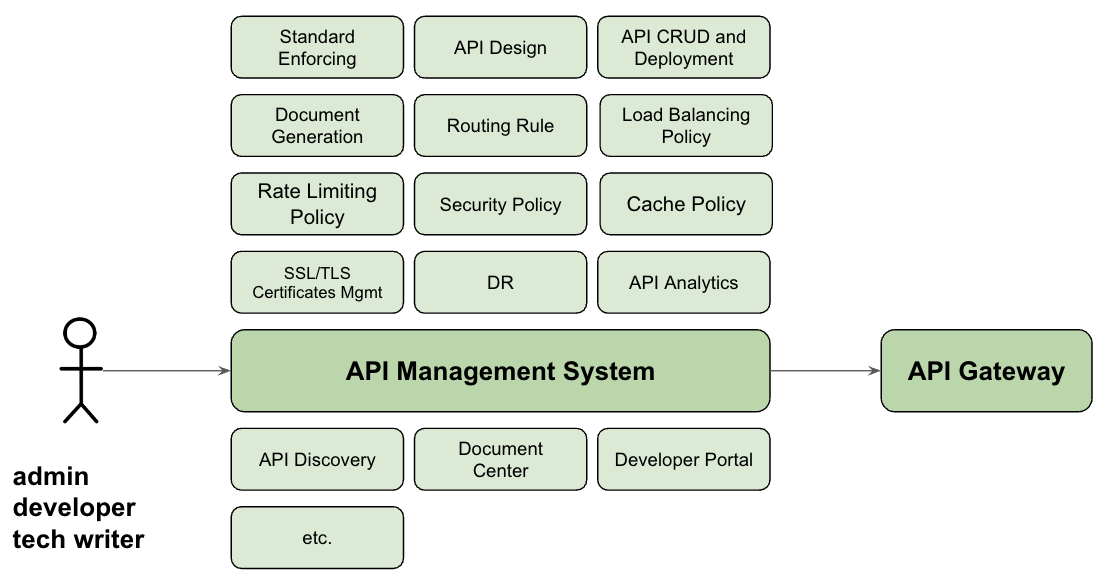
API management system and API gateway are two different components of an API infrastructure that serve distinct purposes but often work together to create a comprehensive API management solution. As one might expect, API management system interacts with API gateway, either directly or indirectly, to configure gateway instances and retrieve API logs/metrics. This collaboration allows for seamless management of API traffic and provides valuable insights into API usage, performance and errors.
How API gateway and management System helps address the challenges
Scalability
APIs need to be scalable to handle changing volume of traffic and demand.
API gateways can help by providing load balancing, response caching, rate limiting, traffic splitting capabilities, ensuring that APIs can scale horizontally to accommodate growing traffic.
API management systems can work with API gateway to offer auto-scaling features, allowing API infrastructure to adapt to demand automatically.
Performance
API performance directly affects user experience and application responsiveness.
API gateways can help optimize performance by implementing efficient caching, protocol translation, request/response compression, and data transformation.
API management systems can provide performance monitoring tools to track API performance and identify potential bottlenecks.
Availability
High availability is crucial for APIs, as downtime can lead to a loss of revenue, reputation, and customer trust.
API gateways can improve availability by implementing redundancy, fault tolerance, throttling and backup strategies through load balancing, rate limiting, backend service marking down, traffic routing and traffic splitting.
API management systems can provide monitoring and alerting tools to detect and resolve issues before they impact users or their impact goes wild. They can also reconfigure API gateway to reroute and redirect traffic based on DR strategy backed with multiple clusters/availability zones.
Security
API security is paramount to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access.
API gateways can help enforce strong authentication and authorization mechanisms, such as OAuth or API keys, and apply encryption for data in transit. They can also integrate with third-party security systems to provide additional protection against threats like DDoS attacks and data breaches.
API management systems can assist in performing regular security audits, vulnerability assessments, and ensuring adherence to security best practices.
Observability
API observability is crucial for maintaining high-performance, highly available, and secure API ecosystems. It enables API teams to proactively identify and resolve issues, optimize resource allocation, and make data-driven decisions.
API gateways generate detailed logs for each API request and response, including metadata such as timestamps, client IPs, and response codes. This information aids in debugging, troubleshooting, and understanding client behavior and traffic patterns. Some API gateways support distributed tracing, allowing teams to trace individual requests across multiple services and components. This helps in identifying performance issues and understanding the dependencies between various applications.
API management systems aggregate and analyze the data collected from API gateways, providing valuable insights into usage patterns, trends, and performance bottlenecks. Then can send out alerts or notifications based on predefined conditions, such as when specific error rates or response time thresholds are exceeded.
Compliance
API teams must ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements related to data privacy, security, and industry- specific standards.
API management systems help maintain compliance with industry standards and regulations by providing tools for auditing, logging, and monitoring API usage. These tools can help organizations track and report on compliance-related activities, ensuring adherence to legal and regulatory requirements.
Discoverability
API discoverability is essential to enable developers to find and use your APIs effectively and also to enable API clients to locate and access the API endpoints.
API gateways and/or API management systems can provide a central platform for documenting and publishing APIs, making it easier for developers to search, discover and use them. This enhances collaboration, reduces duplication of effort, and improves overall engineering velocity.
Comprehensibility
An easy-to-understand API is more likely to be adopted and used correctly by developers.
API management systems can help improve comprehensibility by adopting standard like OpenAPI specification, enforcing consistent API design, providing tools for generating and maintaining documentation, and promoting best practices in API development. This ensures that APIs are easy to understand, reducing the learning curve for developers.
Interoperability
Interoperability is crucial to ensure that APIs can be easily integrated with various systems and platforms.
API gateways can help facilitate seamless integration by supporting widely accepted standards, such as REST, GraphQL, or gRPC, and offering standard data formats like JSON or XML through protocol translation and data transformation. They can also extend the support of integration with diverse backend systems through plugin mechanisms.
Engineering Velocity
API teams need to maintain a high engineering velocity to stay competitive, reduce time-to-market time, deliver value to their users and businesses.
API management systems can help improve engineering velocity by providing automation tools for development, deployment, and monitoring processes, documentation generation, as well as reusable components and templates. They help adopt, enforce and promote standards for API design and documentation. All these frees up developers to focus on writing code, reducing the time it takes to deliver new features and enhancements.
Engineering Quality
Ensuring high engineering quality is essential to prevent issues, minimize technical debt, and maintain a reliable API.
API gateways and management systems can help maintain high engineering quality by offering tools and features that help improve the quality of API development, such as automated testing, versioning and change management. These features ensure that APIs are reliable, stable, and maintainable, reducing the likelihood of errors and downtime.
In Conclusion
API gateways and management systems play a critical role in addressing the key concerns of API teams. By leveraging these tools, organizations can ensure that their APIs are scalable, performant, secure, and compliant, while also improving developer productivity and overall engineering quality.